Entomologia Generalis: Invasiveness, biology, ecology, and management of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda
(草地贪夜蛾的入侵、生物学、生态学与防治)
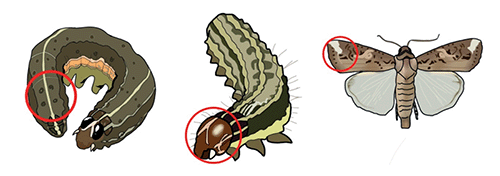
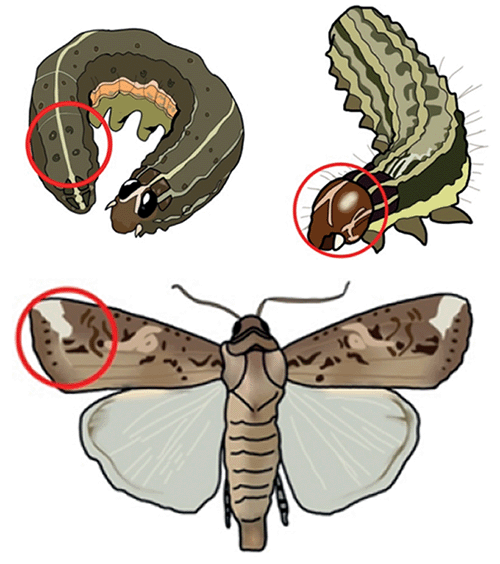
Typical morphological marks on medium to large-sized larvae of S. frugiperda (a square of 4 pinacula on the 8th terga and an inverted Y shape on the head) and white spots on the tip of the forewing of male moths (© Alice De Araujo).
草地贪夜蛾(Fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda)是几种作物上的重要害虫,尤其是玉米和其他谷物。草地贪夜蛾在美洲为害已久,草地贪夜蛾在最近6年时间内,入侵了几乎所有非洲地区、部分中东地区、亚洲以及澳大利亚。其作为入侵物种在全世界很多地区造成了重大损失,这使得我们迫切需要深入理解草地贪夜蛾的各个方面,且在该需求的推动下目前已开展了大量研究。本文对草地贪夜蛾进行了全方位的综述,覆盖了(i)分类学、生物学、生态学、基因组学和微生物组学;(ii)全球形势和区地理扩散;(iii)地域扩张潜力和适当的检疫措施,以及(iv)防治策略,包括监控、采样、预报、生物防治、生物源杀虫剂、农业生态策略、化学防治、杀虫剂抗药性、杀虫剂对自然天敌的影响以及传统和转基因抗性品种。最后我们总结了在入侵地区提高草地贪夜蛾可持续管理能力的研究建议。
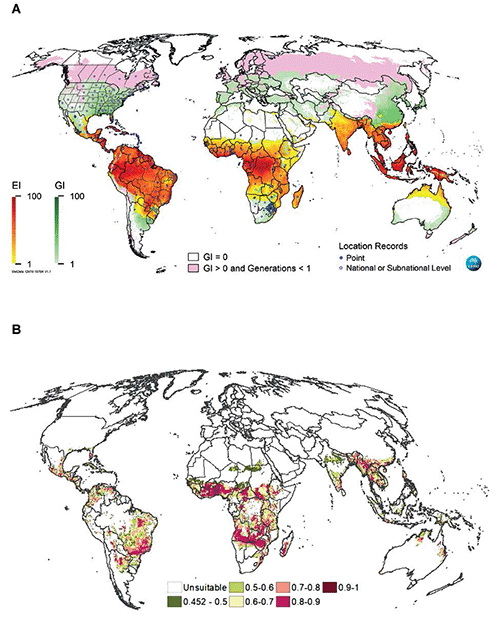
The fall armyworm (FAW), Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith, 1797), is a serious pest of several crops, particularly maize and other cereals. It has long been known as a pest in the Americas and has invaded most of Africa and parts of the Middle East, Asia, and Australia in the last six years. Its new status as an invasive species causing serious damage in many regions worldwide has highlighted the need for better understanding and has generated much research. In this article, we provide a comprehensive review of FAW covering its (i) taxonomy, biology, ecology, genomics, and microbiome, (ii) worldwide status and geographic spread, (iii) potential for geographic expansion and quarantine measures in place, and (iv) management including monitoring, sampling, forecasting, biological control, biopesticides, agroecological strategies, chemical control, insecticide resistance, effects of insecticides on natural enemies, as well as conventional and transgenic resistant cultivars. We conclude with recommendations for research to enhance the sustainable management of FAW in invaded regions.
编辑:吕长宁
原文信息:Kenis, M. et al. Invasiveness, biology, ecology, and management of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomologia Generalis, doi:10.1127/entomologia/2022/1659 (2022).






发表回复